Mayer - Rokitansky - Kuster - Hauser syndrome
Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser syndrome is characterized by the congenital absence of the vagina and uterus. The vagina may look like a dimple with the presence of rudimentary uterine primordia and normally functioning ovaries. Its incidence is 1 in 4500 to 5000 women. Patients present with primary amenorrhea, normal external genitalia, and well-developed secondary sexual characteristics, with a normal female phenotype and karyotype of 46XX. This rare anomaly of the female genital tract is caused by embryologic underdevelopment of the Müllerian duct with subsequent vaginal and/or uterine agenesis.
Treatment of vaginal aplasia consists in creating neovagina for sexual intercourse. This should be offered to women when they are emotionally mature and ready to begin sexual activity. Treatment can be nonsurgical or surgical.
There are several known methods suitable for vaginal reconstruction in Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser syndrome.
Non-surgical treatment
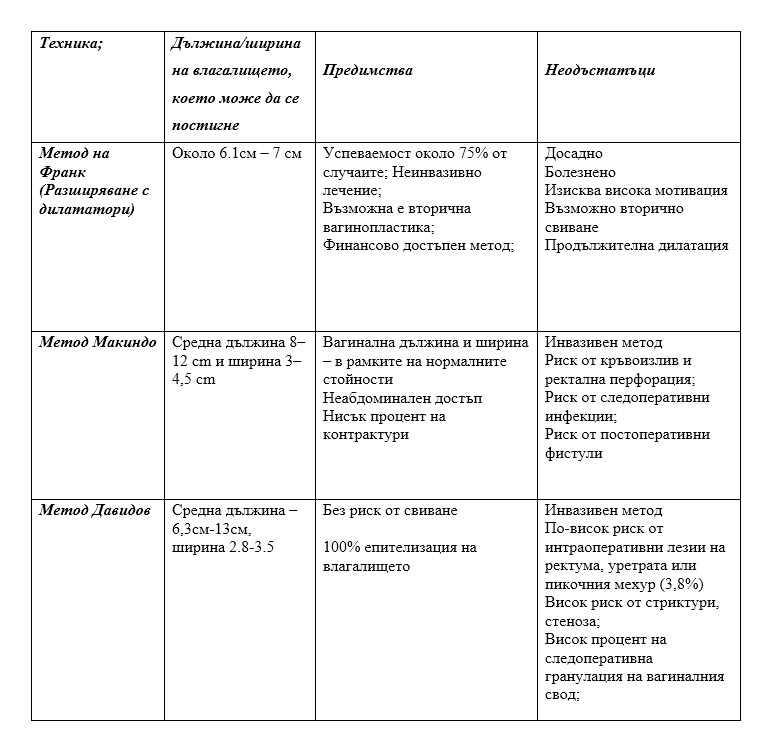
Nonsurgical vaginal dilation for vaginal agenesis involves the use of vaginal dilators of increasing width and length to successfully create a neovagina. This gradually increases the length of the vagina. The dilation treatment is known as Frank's method. It may take several months. The procedure requires high motivation on the part of patients as it is painful and requires persistence. Secondary narrowing of the vagina may occur if the guidelines are not followed. Specialized emotional and psychological support should be planned in vaginal reconstruction approaches along with expert medical care
Surgical treatment
The vagina can be reshaped with reconstructive surgery, but this procedure is complicated. Laparoscopic surgery is used because the lower third of the vagina is at a certain level. The most commonly used laparoscopic methods for established Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser syndrome are:
-
The Mackindo method
One of the most used surgical procedures for vaginal restoration. It consists of performing a careful dissection between the bladder and the rectum, thus creating a cavity that will be shaped by inserting a vaginal mold covered with a skin graft. A skin graft is removed from the inner thigh or buttock and applied over an inflatable penile-shaped prosthesis. Dissection of the vaginal canal begins with a curved incision of the lining of the vaginal introitus.
Dissection is continued by following a plane of cleavage between the bladder and rectum towards the peritoneum, taking care not to injure the bladder or rectum. Gentle blunt dissection is all that is necessary to create a proper cavity. The form covered with the skin graft is inserted into the cavity. To keep the shape in place, the labia majora are sutured along the midline with interrupted sutures. The sutures are excised and the mold is removed for cleaning after 7 days. Initially, the patient keeps the mold in place day and night. After four weeks, sexual intercourse can take place. The patient continues to use the mold at night for about three months. The problem with this technique is that it leaves scarring and long-term expansion of the mold is necessary.
-
The Davidov method
It is a laparoscopic technique to reconstruct the vagina. It is suitable for women in whom dilator dilation has not been successful. Surgical treatment is not a "quick" cure and maintenance of the result obtained with dilators is required. It is preferable to have the operation in late adolescence when the patient is more mature and can follow the recommendations strictly.
Before surgery, it is necessary to do an ultrasound, as well as an MRI of the pelvis and urinary tract. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. The Davidow procedure is a laparoscopic operation. This technique is a three-stage surgery that involves dissection of the rectovesical space, abdominal mobilization of the peritoneum to create vaginal fornices, and attachment of the peritoneum to the introitus. The peritoneum is incised transversely. The incision extends horseshoe-shaped into the connective tissue that separates the bladder from the rectum. The incision is placed over the pelvic peritoneum to make the peritoneal portion of the vagina. Single sutures strengthen the vagina and peritoneum of the pelvic wall.
The patient remained in the hospital for about 7 days. Treatment continued with dilators to maintain the result. Depending on the woman's condition and whether or not she has had sexual intercourse before surgery, sexual life is resumed between 4 weeks to 3 months after surgery after permission from the attending physician.
Other surgical methods that have been described in the literature are:
- Method of William - The Villa vaginoplasty is a technique in which the labia minora are sewn together to create a pocket that becomes the neovagina. However, the resulting neovagina is too small to allow sexual activity without injury or pain. As a result, several modifications have been made, one of which also involves the use of labial tissue to form a deeper pouch that allows for comfortable intercourse.
- Wharton Method - Sheares- George- a minimally invasive surgical approach to creating a neovagina, extremely easy to perform. The rudimentary müllerian canals are gradually dilated by pushing the Hegar dilators in the direction of the pelvic axis, and the resulting medial edge is then transected using diathermy. A vaginal mold is then inserted into the newly created cavity and held in position with two sutures.
- Vecchietti method- In this method, a combination of dilation and non-graft surgery is applied.
The table shows the most commonly used methods for the treatment of Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser syndrome with their advantages and disadvantages.