Cengiz Çabukoğlu successfully cures diseases:
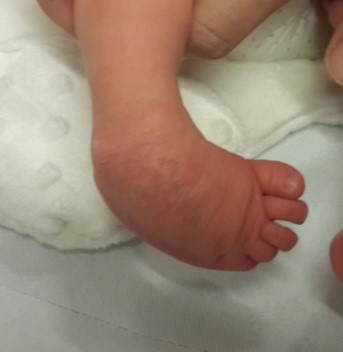
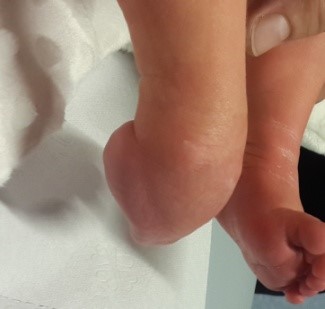
Pes equinovarus (Congenital crooked foot)
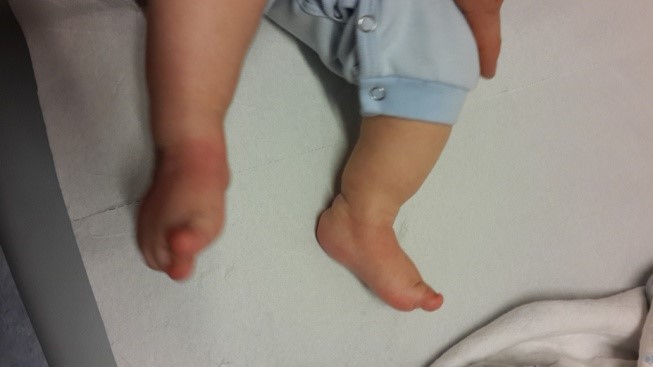
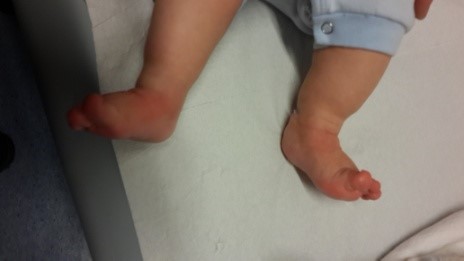
Pes equinovarus (Congenital crooked foot): steep varus position of the calcaneus and of the sole, supination position with medial luxation of the os naviculare associated with adduction position of the mediodorsal part of the sole and joints, delayed development in the differentiation of the skeleton of the sole and disorders in the musculature of the lower leg.
Treatment should begin immediately after delivery. The pedicle is then soft and amenable to modeling.
The deformity of the foot is congenital inward and downward.
It is observed with an average frequency of 1/1000. The soft tissues (muscle tendons and ligaments) on the inside of the foot are stretched, and the bone structure is deformed.
The reason is unclear.
The treatment conducted by Dr. Cengiz Çabukoğlu:
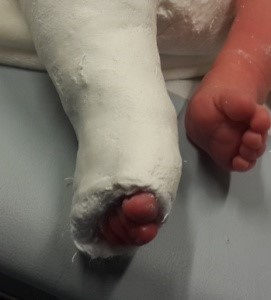
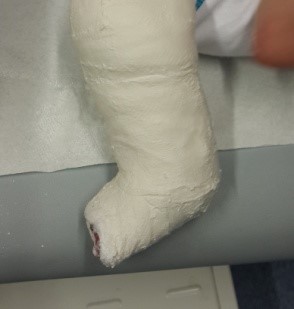
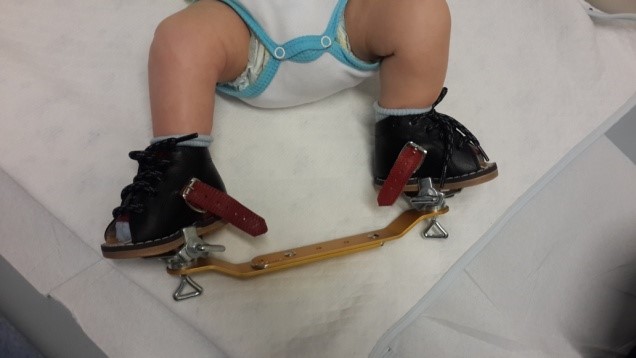
As soon as the baby is born, treatment begins. In the treatment, plaster bandages are made according to the Ponseti method. In this way, a passive stretching is performed on the soft tissues (skin, ligament, capsule, ray, muscle), which are shortened in the posterior and internal part, as well as in the arch of the foot.
Thus, the plaster bandage is made 5 to 8 times, changing it once a week. If the calcaneus bone is not lowered to the level of the base of the foot after casting with a cast (it varies according to the tissue tension in patients), a small surgical intervention is performed under anesthesia and the heel is lowered to where it should be. This intervention is necessary in most cases.
Ponseti's device is subsequently used to prevent the legs from returning to the starting position. Stretching exercises are also continued daily.
In case of return of the foot to the starting position, the intervention must be repeated.
Therefore, the child should be examined periodically (even when the treatment is over) as the child grows, preferably an examination by a pediatric orthopedic doctor.
Arthrogryposis
It is a non-progressive syndrome characterized by non-progressive multiple congenital joint contractures. The etiology of the disease is unknown and is most commonly seen in the absence of fetal movements. It may be due to neuropathic or muscular pathologies, connective tissue disorders, narrowing of the uterine cavity, intrauterine vascular insufficiency, or maternal disease.
The treatment conducted by Dr. Cengiz Çabukoğlu:
In patients diagnosed with arthrogryposis multiplex congenita, treatment should be started early and continued for life. The family should be referred for genetic counseling and a prognosis of the disease should be made. Treatment should have a multidisciplinary approach including physiotherapy and orthopaedic surgery.
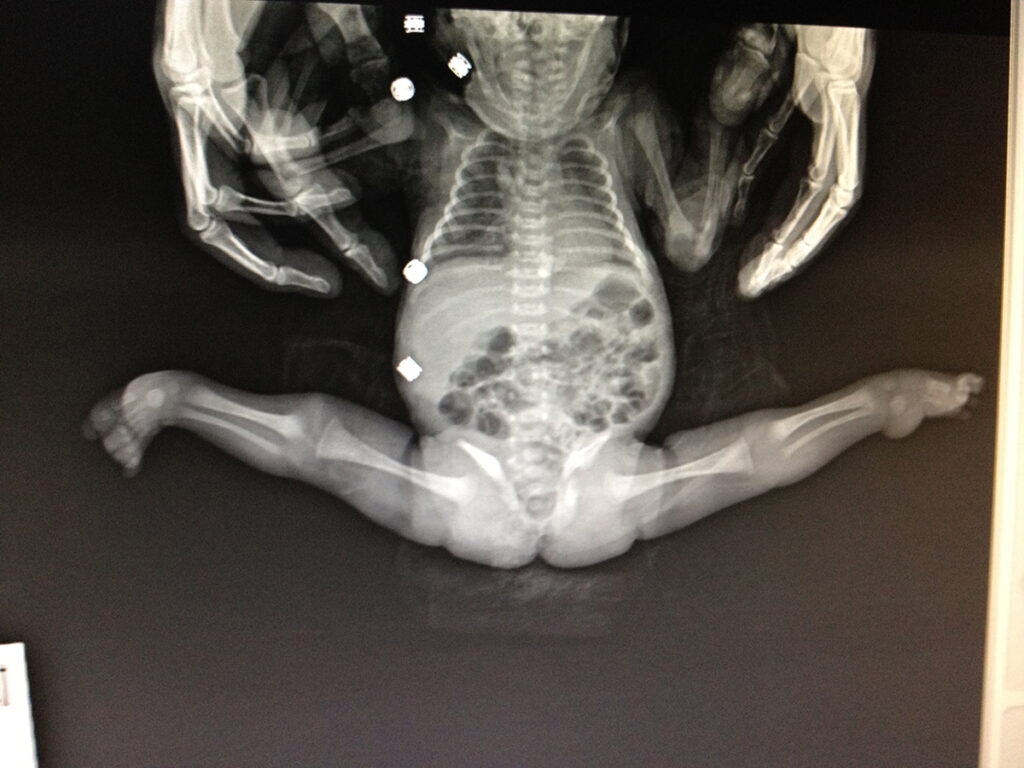
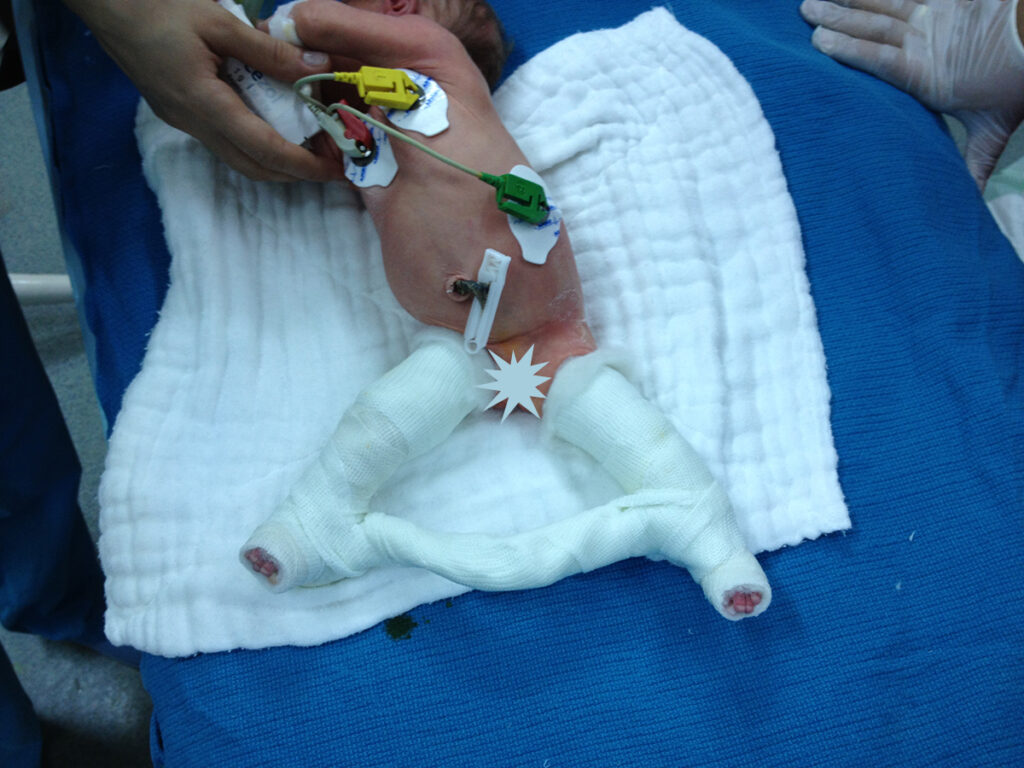
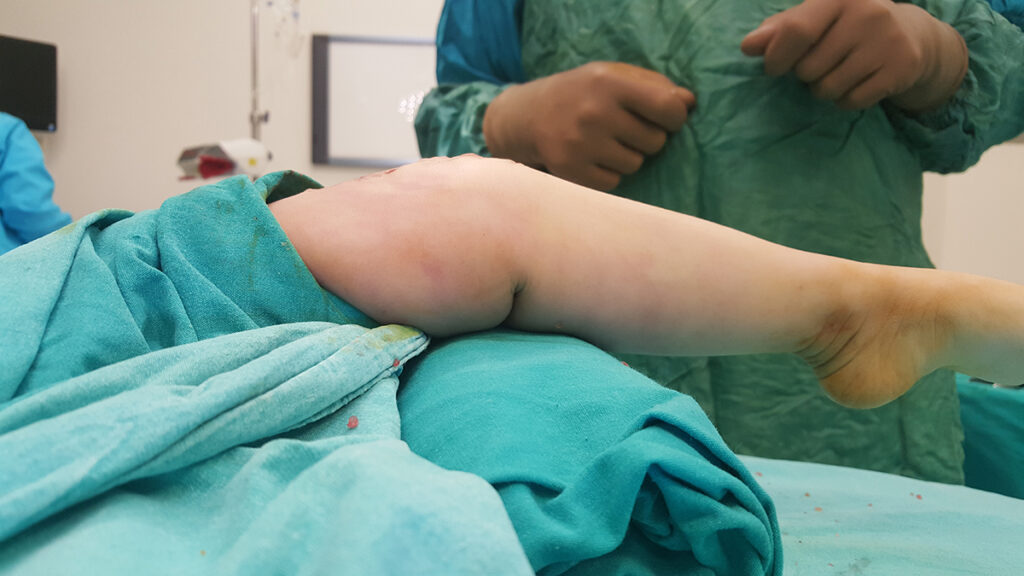
Congenital dislocation of the knee
Congenital knee dislocation is a very rare deformity. At birth, hyperextension of the knee deformity (inversion of the knee) is present. The cause is unclear. It is associated with musculoskeletal abnormalities such as concomitant hip dysplasia and foot dislocation. It is usually treated non-operatively through an individualized plan for each patient.
Before surgery
After surgery
Cerebral palsy
What is cerebral palsy? What are the treatments?
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a permanent disorder of movement and posture due to damage to the brain. Lesions in the brain cause problems in muscle tone and coordination, and over time secondary disorders develop in the musculoskeletal system. CP is seen in brain lesions that occur before, during or after birth. Although early brain development is during the first 18 months, all non-progressive brain lesions occurring by age 6 can be defined as CP. In addition to neuromotor control impairment, CP can also have visual, speech, swallowing and cognitive dysfunctions.
Epidemiology: Although it varies by country around the world, its incidence averages 2-3/1000. The incidence of CP has not decreased over the last thirty years, despite the degree of development of countries and advances in medical technology. This situation is due to the fact that premature and low birth weight babies, who previously had a low survival rate, are still alive today.
Problems can range from mild to severe.
There is no method to completely cure the disease. However, it is aimed that affected patients can meet their needs, sit, walk, attend school independently and have a job according to their condition.
Problems that may be seen in cerebral palsy:
- Difficulty in movement
- Spasticity (excessive muscle tension)
- Muscle weakness
- Imbalance
- Unwanted movements
- Coordination problems
- Attention and perception disorders
- Garches
- Visual impairment and strabismus (strabismus)
- Hearing problems
- Difficulty of speech
- Malnutrition and stunting
- Physical disability (balance and movement difficulties)
- Social and mental disorders
EARLY SYMPTOMS
- 0-1 month - Problem in suckling, excessive vomiting.
- 2nd month - Axial hypotension.
- 3rd month - Delayed head retention and stability in the posture of the child sitting on the mother's knees.
- 4th month - Increased muscle tone of the flexors of the hand - thumb tight in a fist - strabismus.
- 8th month - They do not turn from stomach to back, they do not sit down, legs cross each other in a sitting position.
- Ten months - Lack of ability to stand, do not respond when called by name, cross legs while standing.
- 1 year - Diagnosis is significantly easier at this stage. Muscle weakness. Along with difficulty with movement, there is almost always muscle weakness. Especially children who cannot hold their head upright when sitting, they fall forward. There is spastic hemiplegia with decreased muscle strength, increased muscle tone more in the flexors of the upper limbs and the extensors of the lower limb, an increase in normal and the presence of pathological reflexes.
Excessive tension and increased muscle tone is called spasticity. A spastic child is not a child with mental retardation, but a child who cannot control his movement due to tension in his muscles. Spasticity makes it difficult for the child to care or makes movement difficult.
Treatment plan:
Physical therapy should begin immediately after diagnosis.
Goal: to increase muscle development, joint balance and coordination and prevent contractures.
Control and treatment of pathologies (seizures, vision problems, hearing problems, malnutrition, dental problems) should be carried out regularly.
Reduction of muscle contractions by performing rhizotomy in selected patients through brain surgery.
Physical therapy should continue with the family, physical therapist, and the child's adaptation immediately after diagnosis.
Orthopaedic interventions:
Up to 5 years of age
- Application of Botox when necessary
- If there are disorders in the bones and joints, surgery can be performed according to the results of the examination and radiography.
After 5 years
- Soft tissue relaxation surgeries (muscle and tendon lengthening)
- Tendon transfer (correcting muscle balance by tendon transfer)
- Osteotomies (the bone is cut and re-fixed in the desired position to bring the bone into the desired position)
- Dislocation operations (operations for radial dislocation of the head of the hip and elbow)
- Arthrodesis (only surgery to fix the affected joint due to joint deterioration and inability to use it properly)
Purpose of treatment:
According to the degree of impairment of the child with cerebral palsy, to improve posture, facilitate care, improve better mobility and provide independent movement and improve social relationships in the community. This should only be accompanied by teamwork across many disciplines (physical therapy, orthopedics, psychology, pediatric neurology, etc.). The child's family and child involvement.
Before surgery
After surgery
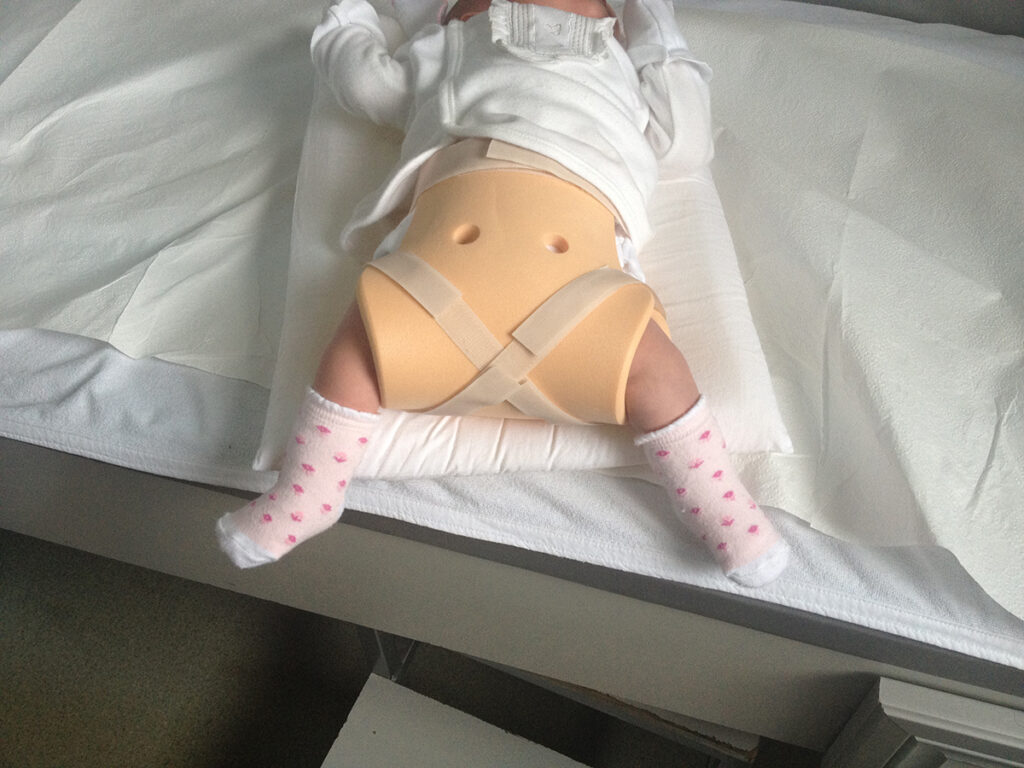
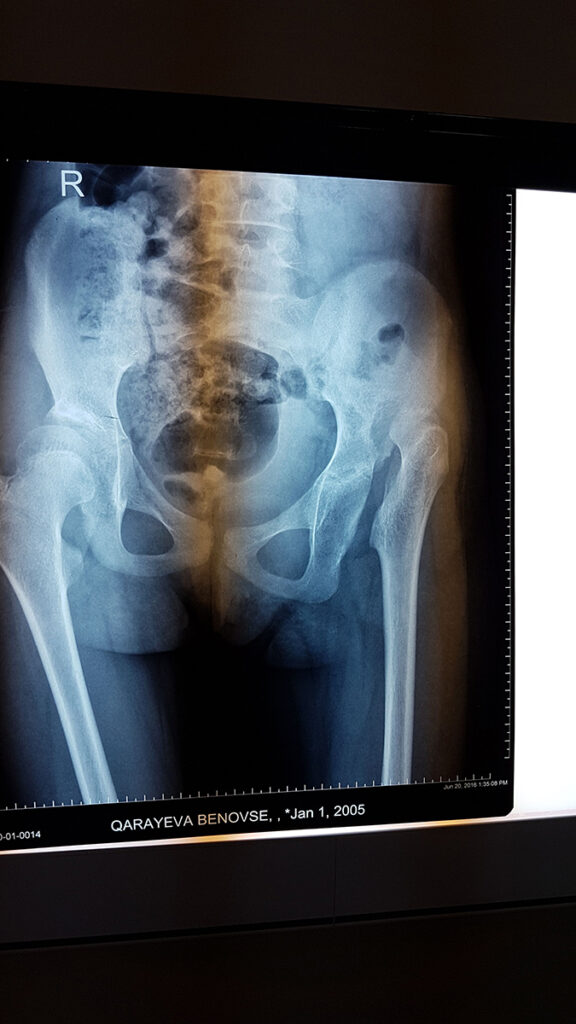
Hip dysplasia (DDH)
This is an orthopedic problem that can come in many forms, from an unstable hip joint to a complete dislocation, which is known as congenital hip dysplasia. Much of DDH can be treated thanks to the ability to diagnose it early, through ultrasound examination of the hip joints of newborns. For this reason, hip ultrasound is performed as a screening test in all newborn infants during the first month, and at-risk infants are followed by an orthopedic surgeon.
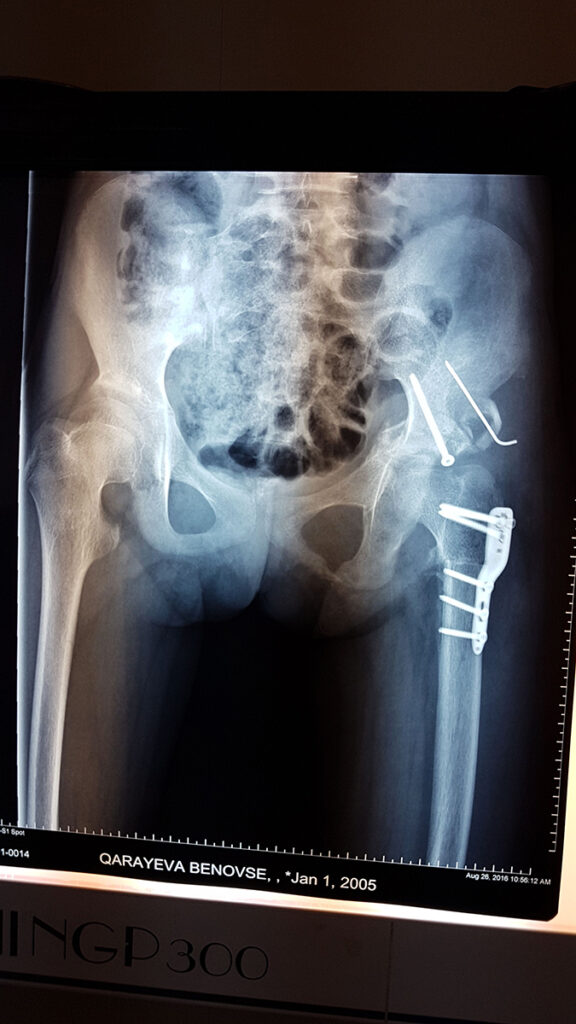
While treatment is carried out in babies who are diagnosed in the early period, through functional pants, patches, then at an advanced age surgical intervention is required. In this case, however, the risk of restriction of hip movements and a violation in the blood supply to the bones and joints, leading to the so-called - avascular necrosis, increases.
Even with complete, successful treatment, annual preventive examinations and follow-up are necessary until the child's growth is complete.