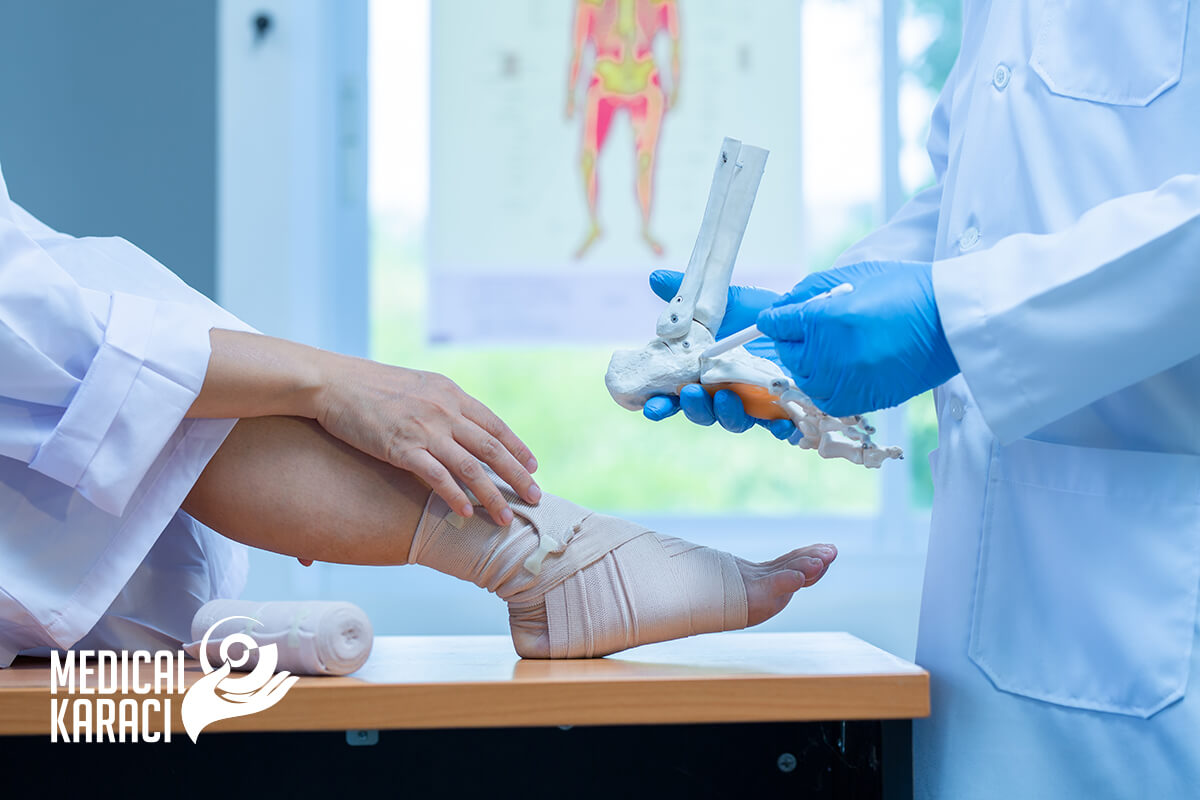
Orthopedics is a branch of medicine that deals with the prevention, diagnosis, treatment of deformities and functional disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Traumatology is the branch of medicine that studies injuries and related diseases, develops methods for the treatment and prevention of injuries.
Orthopaedics and traumatology are interrelated and use common methods and practices.
The term "orthopaedics" is composed of two Greek words - "upright" and "child". Modern orthopaedics corresponds very little in its content and tasks to the literal meaning of its name. The age range of orthopaedic patients is extremely wide-from the first day after birth to old age. This places before the modern orthopaedic traumatologist the requirement for a broad general medical culture and the need for knowledge in a number of fields of medicine.
Orthopedics is a branch of medicine that deals with the prevention, diagnosis, treatment of deformities and functional disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Traumatology is the branch of medicine that studies injuries and related diseases, develops methods for the treatment and prevention of injuries.
Orthopaedics and traumatology are interrelated and use common methods and practices.
The term "orthopaedics" is composed of two Greek words - "upright" and "child". Modern orthopaedics corresponds very little in its content and tasks to the literal meaning of its name. The age limits of orthopaedic patients are extremely wide - from the first day after birth to old age. This places before the modern orthopaedic traumatologist the requirement for a broad general medical culture and the need for knowledge in a number of fields of medicine.
Causes of orthopedic diseases:
- Injuries - traumas
- Congenital anomalies in development
- Overload, degenerative changes
- Inflammation
- Neurological functional disorders
- Systemic diseases
- neoplasms - tumours
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system:
- Degenerative diseases:
- arthrosis disease
- spondyloarthritis
- osteochondrosis
- gonarthrosis, coxarthrosis, omarthrosis, arthrosis of the elbow joint and small joints of the hands and feet
- discopathy, disc herniation
- Inflammatory diseases of the joints and soft tissues:
- rheumatoid and gouty arthritis
- psoriatic arthritis
- ankylosing spondylitis of Bechterew
- arthritis in collagenoses and other internal diseases
- insertionitis, bursitis, periarthritis
- infections
- Traumatic injuries:
- fractures
- luxations
- distortions
- Zudek syndrome
- lesions of the menisci and damage to the capsuloligamentous apparatus
- sports injuries and disabilities
- Neurogenic functional disorders
- prenatal birth brain damage - cerebral palsy
- birth trauma - obstetric paralysis
- inflammatory - poliomyelitis
- Systemic diseases
- Metabolic disorders - rickets, gout
- hormonal disorders - parathyroidism
- autoimmune diseases
- Tumours - can originate from any tissue: skin, fat, nerves, tendons, muscle, cartilage and bone
- Other diseases:
- scoliosis
- spondylolisthesis
- osteoporosis
- Scheuermann - Mau
- Dupuytren's contracture
To reach an accurate diagnosis in Orthopaedics and Traumatology, the following tests are most often performed:
- X-ray examination
- Computed tomography
- Nuclear magnetic resonance
- Arthrography
- Angiography
- Scintigraphy
- Myelography
- Ultrasound examination
- Arthroscopy
- Electromyography
- Laboratory tests
Basic methods of treatment in Orthopaedics and Traumatology
Orthopaedics is a surgical specialty, yet many minor injuries are successfully treated by non-operative methods. Conservative treatment is preferred in cases where it is medically justified and can be expected to have a positive therapeutic effect.
Conservative treatment
- Medications - painkillers, anti-inflammatory, chondroprotective, antibacterial agents, anticoagulants
- Dressings - plaster immobilization, orthopedic devices, soft immobilization
- Physical therapy
- Prosthetics
All methods of conservative treatment have the task to immobilize, fix, abduct, extend and correct.
Operative treatment
Orthopedic surgeons perform a variety of procedures to repair joints, bones, ligaments, tendons and cartilage. Patients who have suffered trauma, such as in a car accident or sports injury, may need orthopedic surgery to correct broken bones, misaligned joints or torn ligaments. Orthopedic surgeons can also help if you suffer from arthritis, bone disease or genetic deformities.
Operative treatment on bone
Purpose of operative orthopedic bone treatment:
- Leveling difference in lengths
- Correction of axial deviations
- Filling bone defects after trauma, tumors, infections
- Changing the load concentration in the joint - in congenital hip dysplasia, for example, an osteotomy creates a more favourable load distribution
- Resection of tumors
- Stabilisation of bone fragments after fracture
Osteotomy
An osteotomy is an operation in which one or more bones are cut. There are many types of osteotomies that are used to treat various orthopedic conditions and injuries. In most cases, an osteotomy involves removing or realigning part of the bone to correct a problem that affects movement, growth, etc. This type of procedure can be applied to repair a damaged joint or to shorten or lengthen a deformed bone.
Types of osteotomies:
This procedure can fix problems in many different bones and joints. For example:
- Hip: During surgery, the doctor reshapes the hip socket to better cover the head of the hip bone.
- Knee: During an osteotomy of the knee, the tibia (top of the shin) or femur (bottom of the thigh) is cut and reshaped. This takes pressure off the injured side of the knee joint.
- Spine: A wedge-shaped piece of bone from a part of the spine may be removed to correct a misalignment or reduce a curvature.
- Jaw: A mandibular osteotomy moves the jaw into a new position.
- Toe: A segment of bone can be removed from the big toe to straighten it and keep it from digging into the rest of the toe.
- Chin: Plastic surgeons use an osteotomy to narrow a wide or square chin.
Osteoplasty
Osteoplasty is a surgical intervention for bone grafting for bone defects, cysts, pseudarthrosis, etc. A distinction is made between autoplasty (using the patient's own bone) and homoplasty (using cadaveric bone tissue).
Auto Grafts - this means that a bone taken from one place on the patient is grafted to another place on the same patient. The site is called the donor site. The most common donor sites are from the sacrum of the pelvic bones, the metaphysis of the tibia, and the radius.
According to their type, autografts are:
- spongioses - made of spongiosed bone - they are the better option because they have great osteoinductive abilities and fusion occurs quickly.
- cortical - from cortical bone only - have poor osteogenesis and healing is much slower.
- Allograft - this is a bone graft from another person. This method has a number of disadvantages such as transmission of infections, for example. On the other hand, large amounts of bone can be taken in this way, even whole joints, whereas the amount of material taken in autografts is less. All allografts are pre-processed in a special way. Bone incorporation is much slower than with autografts.
Metal osteosynthesis
Osteosynthesis is defined as the fixation of bone. It is a surgical procedure to treat bone fractures in which bone fragments are joined with screws, plates, nails or pins. The broken bone is fixed and can be restored stably in the correct position.
Osteosynthesis or internal bone fixation are not used to treat every type of bone fracture. Osteosynthesis is most appropriate for open bone fractures with concomitant skin or soft tissue injury. It is also the preferred form of treatment for bone fractures with multiple fragments, leg bone fractures, and bone fractures in patients with osteoporosis.
Different methods of osteosynthesis are used, such as osteosynthesis with screws, osteosynthesis with plate, intramedullary osteosynthesis with nails, fixation with Kirschner needle, external fixation devices, etc. The materials used nowadays consist mainly of titanium.
How is osteosynthesis surgery performed?
The location of the fracture and the type of disruption have implications for how osteosynthesis is applied. In addition, the location of the fracture and the general condition of the patient will determine whether the operation is performed under general, spinal or local anaesthesia. The operation can be performed on an outpatient basis.
- Osteosynthesis with screws
In screw osteosynthesis, bone fragments are fixed with screws. For this purpose, a hole is drilled in the broken piece in question. A thread for the screw is drilled into the opposite fragment (tension screw) or a screw with a thread in its end is used directly (bone screws). In both cases, the broken pieces are joined together by tightening the screws.
- Osteosynthesis with plate
Plate osteosynthesis is a procedure in which the broken parts of the bone are fixed with a plate. The surgeon screws, on the broken bone, a suitable plate over the fracture line. The plate is fixed to all the fragments with screws in the bone. In this procedure, the fractured parts are joined firmly together.
- Intramedullary osteosynthesis with nails
Intramedullary osteosynthesis with nails is a procedure in which the medullary cavity is opened. The surgeon makes a channel into which a nail can be driven. This nail connects the bone fragments like an internal splint. The intramedullary nail is stabilized with a cross bolt so that it cannot shift. The nail is positioned correctly using an X-ray image.
- Fixation with Kirschner needles
Kirschner needles are flexible steel needles that are used to fix fractures in small bones, such as a finger or clavicle. When the needles are inserted into the bone, the top end remains outside the bone. After the fracture heals, the needles can be removed. A splint or cast is also placed, as the needles alone are not enough to stabilize the fracture.
- External fixation devices
An external fixation device is an external metal support frame used to fix fractures. The surgeon makes small incisions in the skin over the fracture through which he or she drills holes in the bone. Metal rods are passed through these holes and out of the body. The rods are fixed externally to a metal frame, thus stabilizing the bone fracture from the outside.
What is the success rate of osteosynthesis?
Broken bones are stabilized with the various osteosynthesis procedures until the bones fuse again. In general, bone fractures heal very well with these procedures.
What are the possible complications and risks of this procedure?
Osteosynthesis is one of the standard procedures used to treat fractures and usually proceeds without complications. As with any intervention, surgery can sometimes result in infections, nerve damage, post-operative bleeding or blood clots. In rare cases, ankylosis, osteonecrosis or ligament adhesions may occur.
What happens after surgery?
After surgery, the patient is monitored during the recovery phase when he or she wakes up from the anesthetic. Physiotherapy exercises are started soon after to prevent ankylosis and reduce muscle wasting. The osteosynthesis procedure chosen and the individual healing process will determine if the bone can recover normally. It takes at least six weeks for a bone fracture to heal, but can take several months.
Several factors determine whether the osteosynthesis material can be removed when the fracture is completely healed. The material used (titanium) can remain in your body for life. These days, screws and plates are not usually removed unless there are specific reasons for doing so.
Operative treatment on the joints
Puncture of the joint
What is a joint puncture?
In a joint puncture, a needle is inserted into the joint cavity to inject medicine into the joint for inflammation and pain or to perform aspiration (removal) of fluid from the joint to reduce swelling and pressure on the joint. In addition to being a healing method, puncture can also be used for diagnosis. Joint fluid analysis can help diagnose conditions of unclear origin.
Most often, a puncture is performed on the knee joint, but the procedure can also be done on any other joint - shoulder, elbow, hip, wrist, etc.
A puncture of the joint may be necessary if:
- Joint pain has not improved after making simple lifestyle changes, such as resting the joint, using compression bands or taking anti-inflammatories
- Movement of the affected area may be painful and restricted
- Can help soothe joint pain caused by arthritis, bursitis and other painful inflammatory diseases.
Are there side effects with a joint puncture?
The risk of complications from a joint puncture is very low. However, there may be:
- Bruising
- Swelling
- Inflammation at the puncture site
Synvectomy
A synovectomy is a procedure in which the synovial tissue surrounding the joint is removed. This procedure is usually recommended to provide relief for a condition in which the synovial membrane or lining of the joint becomes inflamed and irritated and is not controlled by medication alone.
Arthrotomy
An arthrotomy is a surgical procedure in which the joint is opened to clean the articular surfaces in inflammation and infection. It can also be applied to diagnose joint diseases.
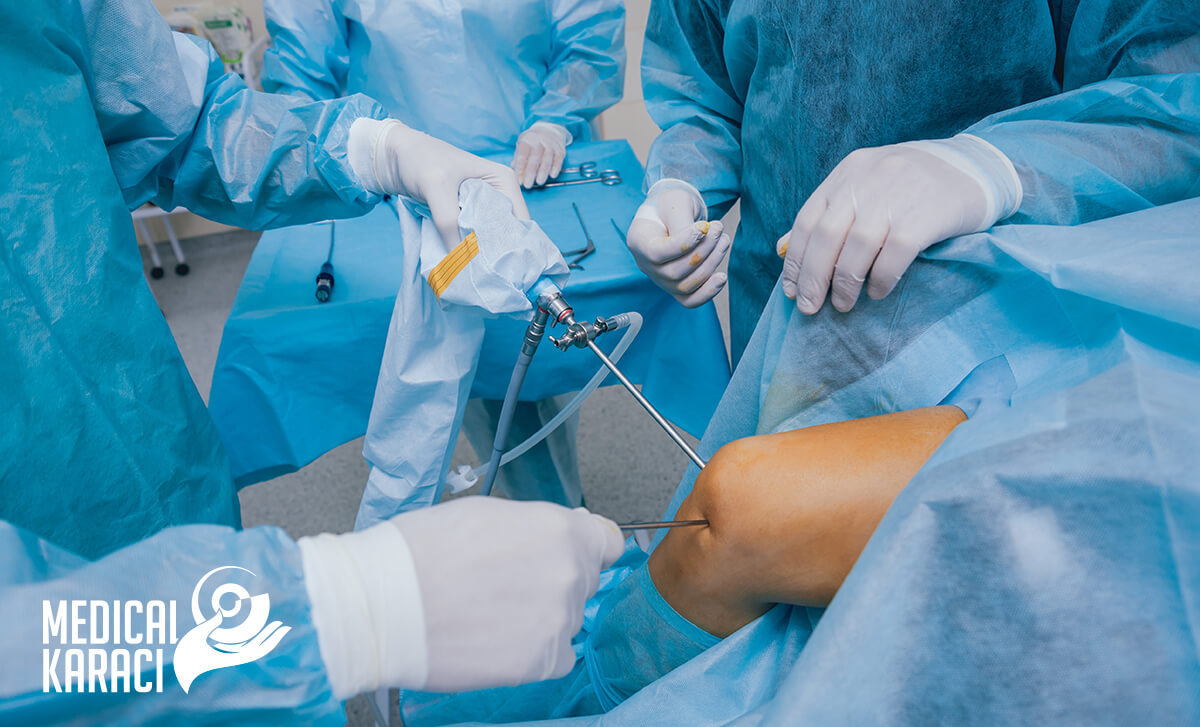
Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is a procedure for the diagnosis and treatment of joint problems. During the procedure, a narrow tube attached to an optical video camera is inserted into the joint through a small incision. The view into the joint is transmitted to a high-definition video monitor.
Arthroscopy allows the orthopaedic surgeon to see inside the joint without making a large incision. Surgeons can even repair some types of joint damage during arthroscopy, with pencil-thin surgical instruments inserted through extra small incisions.
Why is it done?
Orthopedists use arthroscopy to diagnose and treat a variety of joint conditions, most commonly those affecting the knee, shoulder, elbow, ankle, hip and wrist. Doctors often turn to arthroscopy if X-rays and other imaging tests leave some diagnostic questions unanswered.
Surgical procedures
Conditions treated with arthroscopy include:
- Loose bone fragments
- Damaged or torn cartilage
- Inflamed joint surfaces
- Torn ligaments
- Scarring in the joints
Arthroplasty
What is arthroplasty?
Arthroplasty is a surgical procedure to restore joint function, which can be done by resurfacing the bone. An artificial joint called a prosthesis may also be used.
Different types of arthritis can affect the joints. Osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease is the loss of cartilage or cushion in a joint and is the most common cause of arthroplasty.
Why is arthroplasty done?
Arthroplasty can be used when medication treatment no longer effectively relieves joint pain. Some medical treatments for osteoarthritis that can be used before arthroplasty include:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Medicines for pain
- Limiting painful activities
- Assistive devices when walking as a cane
- Physiotherapy and rehabilitation
- Injections of cortisone into the knee joint
- Viscosupplementation injections (to add lubrication to the joint to make joint movement less painful)
- Weight loss
Patients who undergo arthroplasty usually experience significant improvement after the procedure. Joint pain is significantly reduced, the ability to perform various activities is restored and quality of life is improved.
Most joint surgeries involve the hip and knee, with ankle, elbow, shoulder, and finger surgeries done less frequently.
Arthrodesis
Arthrodesis is also known as syndesis or artificial ankylosis. It is also commonly called a joint fusion. It is a method of surgically ossifying joints used to fuse bones in a joint when other treatments do not produce positive results.
Arthrodesis is used to treat joint fractures, arthritis and other conditions that affect joint mobility. If pain cannot be managed through other treatments, arthrodesis may be the best solution. However, doctors believe that arthrodesis is a treatment of last resort that is only administered after other options have been exhausted. The best candidates for joint fusion are those who still have healthy bones on both sides of the joint and a strong immune system to aid in healing.
Joint replacement or Arthrodesis
The arthrodesis procedure fuses the bones of the joint and prevents movement in that joint. Joint replacement surgery replaces the damaged joint with an artificial one. These artificial joints have the same range of motion as natural joints, but can also wear out quickly. Additional surgeries may be needed in the future. For this reason, joint fusion is often a better and more permanent solution for joint pain.
In arthrodesis, incisions are made around the joint and all the cartilage in the joint is removed so that the bones touch directly. The joint is then secured with metal plates and screws. This allows the bones to heal and fuse together to create an immovable joint. Because fusing the bones eliminates movement in the joint, the procedure is best suited for treating areas of the body that can still be used without full range of motion. For example, ankle arthrodesis is done more often than joint fusion in the knee or hip
Arthrolysis
Arthrolysis is a surgical procedure to treat conditions that cause stiffness and significantly reduced range of motion in joints. Physical therapy is critical before and after arthrolysis to maximize range of motion and function in the operated joint.
Joint stiffness is a common problem that has been linked to numerous conditions, including osteoarthritis, fractures and other injuries, as well as complications resulting from previous surgeries and treatments. Arthrolysis surgery is needed to increase range of motion and function in an affected joint. Arthrolysis involves the release of any soft tissues that interfere with full range of motion in a joint. During arthrolysis, a number of small incisions are made on the sides and back of the joint. The restricted joint capsule and contracted tissues are released to allow more movement. The outer (lateral) side of the joint is released first and any adhesions are separated. Then the restricted joint capsule and the contracted tissues are released from the inner (medial) side of the joint. The medial ligament on the inside is released to further improve the range of motion in the joint. Any bony abnormalities are then treated. Finally, small sutures are used to close the wounds.
Physiotherapy is extremely important before and after arthrodesis to ensure that the operation is successful, to prevent the likelihood of problems in the future and to ensure the full or near full return of full range of movement and function to the affected joint and therefore the whole limb.
Aloplasty
Aloplasty means a surgical operation to replace a joint or part of a joint with a prosthesis. The medical term endoprosthesis is also used. The most common materials for alloplasty are metal and plastic (splints, screws, stents, etc.). All metals used are made of a special alloy and non-magnetic material. Its implantation and fixation in the tissue prevents unwanted movement or sliding in the joint.
Total replacement of the injured joint is indicated in cases where conservative treatment is unsuccessful. This is a condition in which the functionality of the joint is significantly impaired or the joint is a source of severe pain. The most common reasons for surgery are arthrosis - coxarthrosis, gonarthrosis, bone tumor, fractures, reimplantation and others.
Operative treatment on fascia, tendons and muscles
Fasciotomy
A fasciotomy or fasciectomy is an operation to relieve swelling and pressure in an affected part of the body- tissue or muscle. The fascia that surrounds the area is cut to relieve the pressure.
Tenotomy
A tendon release, also known as a tenotomy, is a surgical procedure that involves cutting or disconnecting the tendon to allow for a greater range of motion. The procedure is used to relieve tight or torn muscles. When the Achilles tendon is affected, the procedure is called an "achilotendotomy." It is used in the treatment of cerebral palsy.
Tenodesa
Tenodesis is a surgical procedure commonly used to treat biceps tendon injuries in the shoulder. These injuries can occur due to tendonitis, inflammation or irritation of the tendon, from overuse or trauma in the shoulder area. Ligament problems can occur anywhere in the body, but are more common in certain joints such as the shoulder due to its wide range of motion. Patients may undergo tenodesis if they experience significant pain and weakness in the shoulder due to biceps tendon injury.
During the procedure, the surgeon removes the damaged tissue around the biceps tendon and separates the tendon from its connection to the labrum of the shoulder joint. Any fragments of bone or cartilage or bone spurs that may irritate the tendon are removed. The tendon is then attached to the humerus near the shoulder joint using anchors and strong sutures to hold it in position. This serves to reduce stress on both the tendon and labrum.
A hospital stay is usually not required after a tenodesis procedure. Patients should wear a sling for several weeks after surgery to provide support and protection to the healing shoulder joint. Physical therapy aids the recovery process as it helps strengthen and restore function to the shoulder. Most patients can return to work after a few days, but it usually takes three to six months before more strenuous activities are allowed.
Tendorrhaphy
Tendorrhaphy is the suturing of a torn tendon due to injury or disease.
Tendon and muscle transpositions
Musculotendinous transpositions are applied when one or a group of muscles permanently lose function due to paralysis, in order to have their function taken over by other muscles. Paralysed muscles are activated if other muscles with preserved innervation are sewn to their tendons. It has been found that if the repositioned muscles are synergistic to the paralyzed ones, the functional outcome is better and occurs faster. If the repositioned muscle is partly synergistic with the paralyzed muscle, it takes over its function more slowly and after a longer period. The adaptation is even more difficult and long if the transposed muscle or muscles are complete antagonists of the paralyzed ones.
For more information, you can call +359895770869.